Accounting and Organizational Internal Controls
One of the best defenses against business failure is having adequate internal controls (IFAC, 2012). Accounting and internal controls are essential to an organization’s governance system and ability to manage risk and prevent fraud. In addition, they support the achievement of an organization’s goals and enhance the creation and protection of shareholders’ value.
What are accounting and internal organizational controls?
Internal controls are a process. They are designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding achieving objectives in the effectiveness and efficiency of organizations’ operations, accuracy and reliability of financial and non-financial reporting, and compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
The management of an organization is responsible for designing, implementing, and maintaining all internal controls. The Board is responsible for the overall oversight of the control environment.
An effective internal control system protects your organization in two ways (AICPA, 2014), i.e., providing:
- Preventive control: These controls are designed to discourage errors of fraud by minimizing opportunities for unintentional errors or intentional fraud that may harm the organization
- Detective control: These controls are designed to identify errors or fraud after it has occurred by discovering minor errors before they become significant errors.
Components of Internal Control
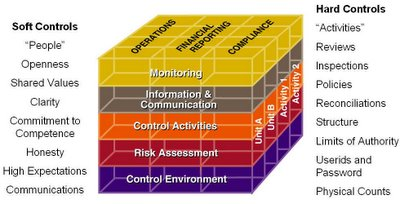
The five components of internal controls include control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information communication, and monitoring (Cerini, 2016). The control environment is the foundation of the other four components. It sets the tone at the top of an organization and provides discipline and stricture.
Factors within the control environment include ethical values and integrity, HR policies and procedures, organization structure, the participation of those charged with governance, philosophy of management and its operating style, and responsibility assignment.
Importance of internal controls
Internal controls help organizations to:
- Efficiency conduct business: They are put in place to ensure that processes flow smoothly and operations mitigate the risks of inefficiencies and threats to creating value in the organization.
- Safeguard assets: Internal controls are designed to protect assets from accidental loss or loss from fraud.
- Ensure the reliability and integrity of financial information: They ensure management has accurate, timely, and complete information, including accounting records, to facilitate planning, monitoring, and reporting of business operations.
- Ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations: They ensure compliance with appropriate local, state, and federal laws and regulations affecting the organization’s operations.
- Promote efficiency and effectiveness of operations: They provide an environment that optimizes operations’ efficiency and effectiveness.
- The accomplishment of goals: They provide a mechanism for the management and monitoring of the achievement of organizational goals and objectives.
- Prevent and detect fraud and other unlawful activities.
Fraud prevention tips
Fraud is an intentionally deceptive action that results in financial or personal gain. In organizations, fraud can be in the form of forgery or alteration of information or document, misappropriation of assets, authorizing or receiving compensations for goods or services not received or performed, and rough handling and reporting of money transactions among others.
What are ways to prevent fraud?
Tips to prevent fraud include:
- Segregation of duties: Assign duties to each employee that divides responsibilities for handling, recording, and auditing. The further apart these functions are, the lower the risk of fraud associated with each.
- Access controls: Set permission levels to safeguard data and physical assets. In password-protected areas, secure passwords and two-step authentication methods will make it difficult for employees to use others’ login credentials. Enable frequent changing of passwords and automation of access logs and usage history that can be audited to find discrepancies.
- Physical Audits of assets: Auditing the most used access internal control.
- Standardized financial documentation: This creates consistency, easing the auditing process.
- Daily or weekly trial balances: Double-entry accounting ensures that the books are always balanced; any discrepancies in entries can easily be detected. The trial balance is an accounting control that provides additional reliability to the system.
- Periodic reconciliations in the accounting systems: Reconciling bank and supplier statements and understanding which items have cleared or not, or are in transit, will allow you to uncover errors and fraud.
- Approval authority requirements: Designate persons (managers) responsible for transaction authorizations. These approvals may follow a hierarchy necessitating two or more layers of agreement before a transaction is finalized.
Implementing efficient accounting and organizational controls is meaningless unless the organization has a procedure to handle problems once they are detected. Therefore, put in place clear policies and processes that give employees the proper direction on responding to issues as they arise.
Article Sources for further reading:
- American Institute of CPAs (2014). The importance of internal control in financial reporting and safeguarding plan assets. (URL)
- Cerini, K. R. (2020, October 23). Key Components of Internal Controls. Cerini & Associates, LLP Blogs. click to access URL
- International Federation of Accountants (IFAC) (2012). Evaluating and Improving Internal Control in Organizations. (URL)
